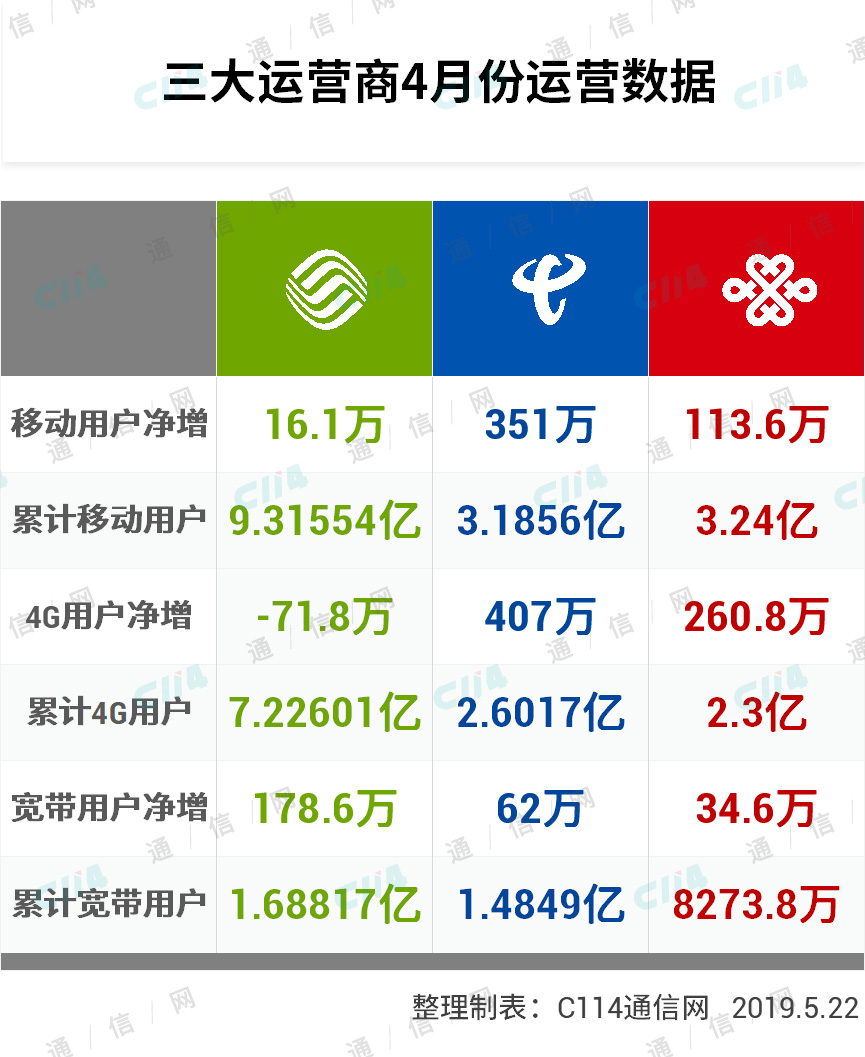
(资料图片仅供参考)
(资料图片仅供参考)
JSONObject只是一种数据结构,可以理解为JSON格式的数据结构(key-value结构),可以使用put方法给json对象添加元素。JSONObject可以很方便的转换成字符串,也可以很方便的把其他对象转换成JSONObject对象。
pom:
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.28</version> </dependency>
1.通过原生生成json数据格式。
JSONObject zhangsan = new JSONObject(); try { //添加 zhangsan.put("name", "张三"); zhangsan.put("age", 18.4); zhangsan.put("birthday", "1900-20-03"); zhangsan.put("majar", new String[] {"哈哈","嘿嘿"}); zhangsan.put("null", null); zhangsan.put("house", false); System.out.println(zhangsan.toString()); } catch (JSONException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }2.通过hashMap数据结构生成
HashMap<String, Object> zhangsan = new HashMap<>(); zhangsan.put("name", "张三"); zhangsan.put("age", 18.4); zhangsan.put("birthday", "1900-20-03"); zhangsan.put("majar", new String[] {"哈哈","嘿嘿"}); zhangsan.put("null", null); zhangsan.put("house", false); System.out.println(new JSONObject(zhangsan).toString());3.通过实体生成
Student student = new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setAge("20"); student.setName("张三"); //生成json格式 System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(student)); //对象转成string String stuString = JSONObject.toJSONString(student);4.JSON字符串转换成JSON对象
String studentString = "{\"id\":1,\"age\":2,\"name\":\"zhang\"}"; //JSON字符串转换成JSON对象JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSONObject.parseObject(stuString); System.out.println(jsonObject1);5.list对象转listJson
ArrayList<Student> studentLsit = new ArrayList<>(); Student student1 = new Student(); student1.setId(1); student1.setAge("20"); student1.setName("asdasdasd"); studentLsit.add(student1); Student student2 = new Student(); student2.setId(2); student2.setAge("20"); student2.setName("aaaa:;aaa"); studentLsit.add(student2); //list转json字符串 String string = JSON.toJSON(studentLsit).toString(); System.out.println(string); //json字符串转listJson格式 JSONArray jsonArray = JSONObject.parseArray(string); System.out.println(jsonArray);阿里的json很好用,还有一个谷歌Gson也不错。有兴趣的可以看一看
到此这篇关于JSONObject用法详解的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助。
关键词: JSONObject用法 JSONObject详解